The future of steel in green construction is bright, driven by the push for sustainable development, technological innovation, and the need to reduce carbon emissions. Steel, a versatile and recyclable material, plays a critical role in the shift toward environmentally friendly building practices. Here’s an overview of its evolving role:

- Sustainable Steel Production
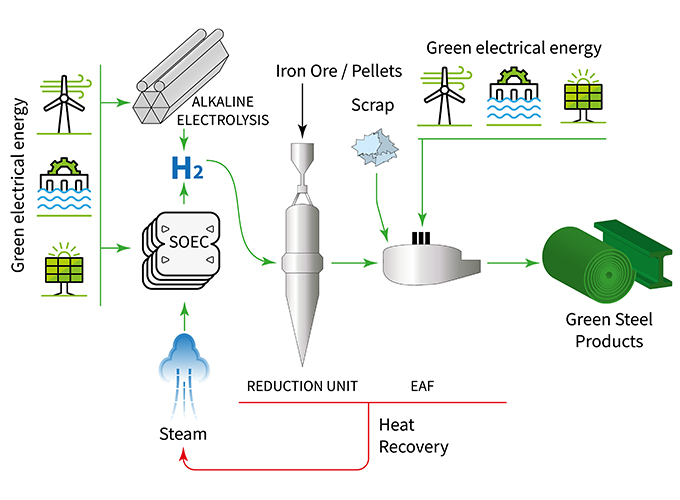
Green Steel Technologies: Innovative methods like hydrogen-based steelmaking and electric arc furnaces powered by renewable energy are replacing traditional blast furnaces, reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): Steel manufacturers are exploring CCS technologies to trap and store CO₂ emissions from production processes.
Recycled Steel: Using scrap steel reduces energy consumption and minimizes the environmental footprint of new steel production.

- Steel’s Advantages in Green Construction
Recyclability: Steel is 100% recyclable without losing its properties, making it a circular material ideal for sustainable construction.
Durability: Its longevity reduces the need for frequent replacements, lowering the overall carbon footprint of buildings.
Lightweight Structures: High-strength steel allows for lightweight designs, reducing the amount of material needed and transportation emissions.
Adaptability: Steel structures can be easily modified or reused, supporting flexible building designs and reducing demolition waste.
- Innovations in Steel Products
Thermally Efficient Steel: Advanced coatings and treatments improve steel’s thermal performance, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings.
Prefabricated Steel Modules: Modular construction using steel components reduces construction waste and speeds up building processes.
Smart Steel: Integration of sensors into steel components enables real-time monitoring of building performance and maintenance needs.
- Applications in Green Building Projects
Energy-Efficient Buildings: Steel is used in passive house designs and net-zero buildings for its strength and energy-saving properties.
Renewable Energy Infrastructure: Steel is crucial for wind turbines, solar panel frames, and other renewable energy systems.
Green Roofs and Facades: Steel supports structures that incorporate vegetation or solar panels, contributing to sustainable urban environments.
- Challenges and Opportunities
Reducing Embodied Carbon: While operational energy efficiency is often prioritized, reducing embodied carbon in steel production is essential.
Cost of Green Steel: Initial costs for green steel production methods may be higher, but economies of scale and policy incentives can make them more competitive.
Government Policies and Certification: Stricter building codes, carbon pricing, and certifications like LEED and BREEAM drive the adoption of sustainable steel practices.

- Future Trends
Collaborations for Innovation: Partnerships between steel manufacturers, construction firms, and researchers are accelerating the development of sustainable solutions.
AI and Digitalization: AI and BIM (Building Information Modeling) are optimizing steel usage, minimizing waste, and improving lifecycle assessments.
Global Commitments: Initiatives like the Paris Agreement and corporate sustainability goals are fostering widespread adoption of green construction materials, including steel.
In summary, the steel industry is undergoing a transformative shift to align with the principles of green construction. Through sustainable production methods, innovative applications, and collaboration, steel is poised to be a cornerstone of eco-friendly infrastructure and buildings in the decades to come.