The steel industry today is undergoing significant transformation as it adapts to modern technological demands, environmental regulations, and fluctuating global economic conditions. Here are some of the main trends and future developments shaping the steel industry:

- Decarbonization Efforts
Current Situation: The steel industry is one of the largest CO₂ emitters globally, responsible for about 7-9% of global emissions. With the global push to combat climate change, pressure is on the steel sector to reduce its carbon footprint.
Future Developments: There is a movement toward “green steel,” which involves using hydrogen-based direct reduction or electric arc furnaces (EAFs) powered by renewable energy instead of traditional coal-based blast furnaces. Companies like ArcelorMittal and SSAB are investing in hydrogen-based steel production processes to lower emissions.

- Increased Recycling and Circular Economy
Current Situation: Recycled steel is already widely used, especially in electric arc furnaces. Using scrap reduces both energy consumption and raw material demand.
Future Developments: The industry is expected to further integrate circular economy principles by increasing scrap use and developing more efficient recycling technologies. This shift will help conserve resources and reduce emissions.

- Digital Transformation and Industry 4.0
Current Situation: Many steel companies are adopting digital solutions, such as automation, robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and Internet of Things (IoT) technology, to enhance production efficiency and reduce costs.
Future Developments: Digitalization will continue to reshape steel production. Predictive maintenance, digital twins, and smart factory concepts are becoming more common, allowing for better monitoring, predictive analytics, and reduced downtime. AI and machine learning could also help optimize production processes, reducing waste and energy use.

- Lightweight and High-Strength Steel for New Markets
Current Situation: Demand for lightweight, high-strength steel is rising, especially in the automotive, aerospace, and construction industries.
Future Developments: Research and development are focusing on creating steel grades that are both stronger and lighter. Advanced high-strength steels (AHSS) and other innovative alloys can provide these properties, offering an alternative to materials like aluminum and carbon fiber in automotive manufacturing.
- Regional Shifts and Market Dynamics
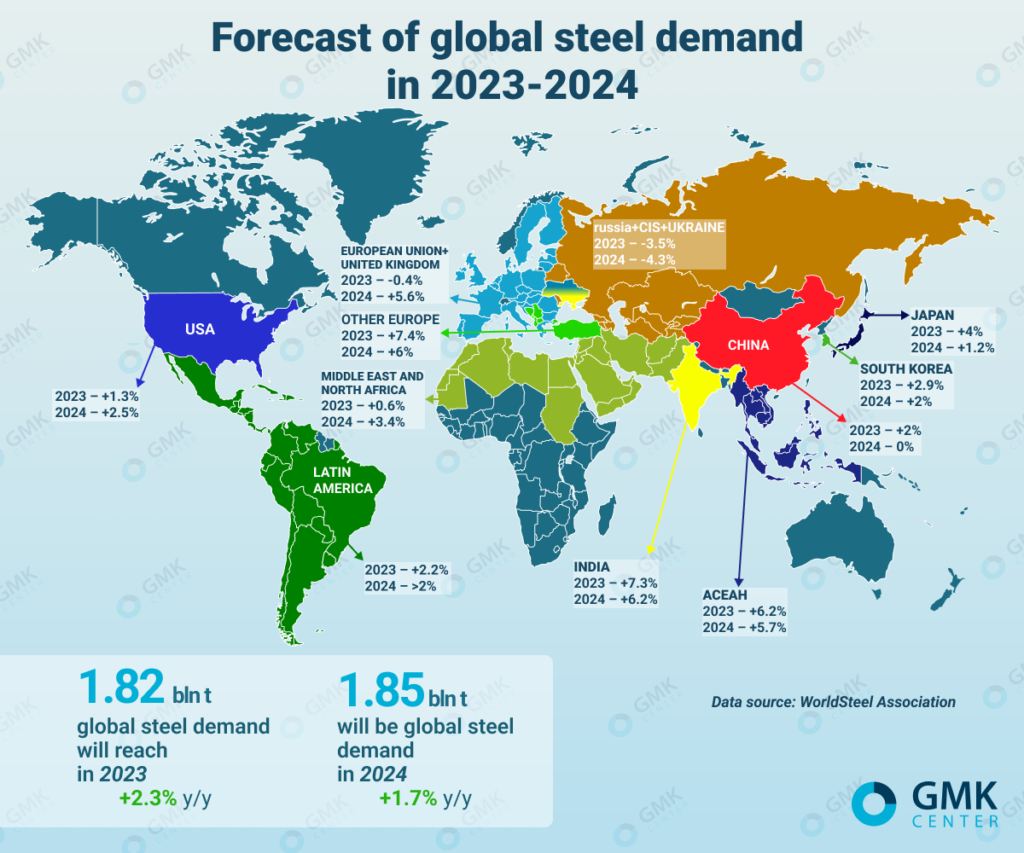
Current Situation: China is the largest producer of steel, but production has slowed as the country focuses on reducing pollution and controlling overcapacity. Other regions, like India and Southeast Asia, are increasing production.
Future Developments: Production is expected to become more regionally diverse. India, with its growing infrastructure needs, is likely to see an increase in steel production and demand. Other emerging economies could also see growth as they invest in infrastructure.
- Supply Chain Resilience
Current Situation: The steel industry has faced supply chain disruptions due to factors like the COVID-19 pandemic, trade tensions, and logistical bottlenecks.
Future Developments: Companies are likely to diversify their supply chains and reduce dependency on specific regions to improve resilience. Localized production and securing alternative raw material sources are likely to be part of future strategies.
- Government Policies and Regulation
Current Situation: Governments are increasingly implementing regulations to reduce emissions and encourage sustainable practices within the steel sector. Carbon taxes, emissions targets, and subsidies for green technology are becoming more common.
Future Developments: Regulatory policies are expected to tighten, pushing the industry towards lower emissions. Carbon pricing mechanisms and clean energy standards will likely continue to influence how steel is produced, driving investment in cleaner technologies and possibly increasing the cost of steel production if emission goals are not met.

- Advances in Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) Technology
Current Situation: EAFs are commonly used to recycle scrap, with less carbon impact than traditional methods.
Future Developments: EAF technology is expected to become more widespread and advanced, especially as renewable energy becomes more accessible. Advances in EAF technology could allow for greater flexibility and efficiency in production, enabling greener and more adaptable steel production.
Summary
The future of the steel industry is leaning towards sustainability, digitalization, and innovation. The shift to greener practices, driven by decarbonization, circular economy models, and energy efficiency, is shaping the sector. While challenges like high initial costs and regulatory pressure remain, the drive for more sustainable production processes and high-performance steel products is setting the stage for the steel industry’s future.