Refractory materials are specialized industrial substances capable of withstanding extremely high temperatures, often exceeding 1,000°C (1,832°F). They are essential in various high-temperature industrial processes where durability, thermal stability, and resistance to chemical attack are required.

Characteristics of Refractory Materials:
- High Melting Point: Withstand temperatures without melting or softening.
- Thermal Stability: Maintain structural integrity under rapid temperature changes.
- Chemical Resistance: Resist corrosion from slag, gases, or molten materials.
- Mechanical Strength: Retain strength under high-stress conditions and thermal cycling.
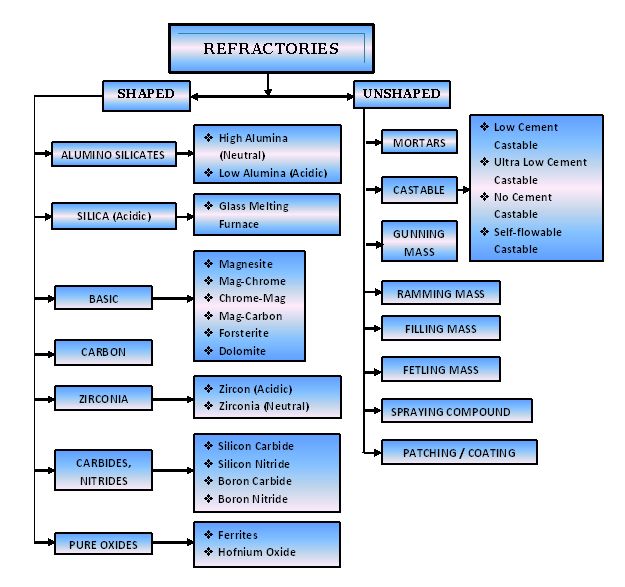
Types of Refractory Materials:
- Acidic Refractories: Made of silica or zirconia; used where acidic environments prevail.
Example: Silica bricks.
- Basic Refractories: Made of magnesia or dolomite; suited for basic environments.
Example: Magnesia bricks.
- Neutral Refractories: Compatible with both acidic and basic conditions.
Example: Alumina and chromite.
Applications:
Steel Industry: Linings for blast furnaces, converters, and ladles.
Cement Production: Kiln linings and coolers.
Glass Industry: Melting tanks and regenerators.
Petrochemical Industry: Catalytic cracking units.
Power Plants: Boilers and incinerators.
These materials are critical for energy efficiency and operational safety in high-temperature industrial applications.